CASE
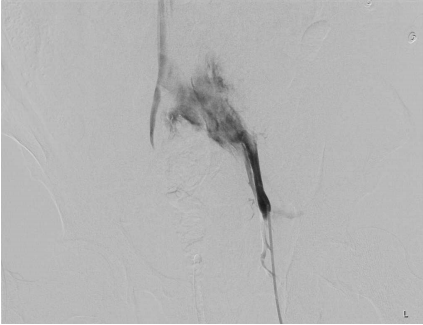
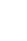
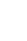
A 64-year-old male patient was transferred to our emergency department. He had experienced a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) (performed owing to cardiac arrest) and was transferred to our hospital. On the abdominal computed tomography (CT) at the original hospital, a contrast leak was observed in the left common iliac vein. After arriving at our hospital, mechanical ventilation was initiated, and cardiac arrest and ROSC occurred twice more. After a massive transfusion, his blood pressure was 96/50 mmHg, and radiologic intervention was performed. Venography, which was done through puncture of the left common femoral vein, revealed rupture and massive extravasation (Fig. 2.). Through a 12F sheath, a 16ŌĆō12 mm/100 mm stent graft (Gore Excluder stent graft) was inserted. Subsequent venography revealed disappearance of the extravasation (Fig. 3.). After the intervention, the patientŌĆÖs blood pressure recovered to 124/70 mmHg, and he underwent no further treatment in the intensive care unit. However, the status of the patient deteriorated, and he died the day after the intervention.
DISCUSSION
Blunt trauma-induced iliac vein rupture is rarely reported [1-3]. Until now, there has been no case report describing stent insertion in an iliac vein in a patient with ROSC after CPR. Endovascular management of iliac vein rupture can be an option to consider for a patient whose hemodynamic status is relatively stable.