 |
 |
- Search
| Trauma Image and Procedure > Volume 4(1); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Biloma is a common complication in patients with traumatic liver injury. Biloma is usually confirmed by abdominal computed tomography (CT), and the first detection using abdominal ultrasonography is rare. We report a case of a patient with American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) grade IV liver injury according to the Organ Injury Scale (OIS) score, who underwent transcatheter arterial embolization on the day of admission and percutaneous drainage after the diagnosis of biloma on ultrasonography on day 5 after admission. In this case, biloma was observed as a hypoechoic to anechoic fluid collection in the hepatic dome on ultrasonography.
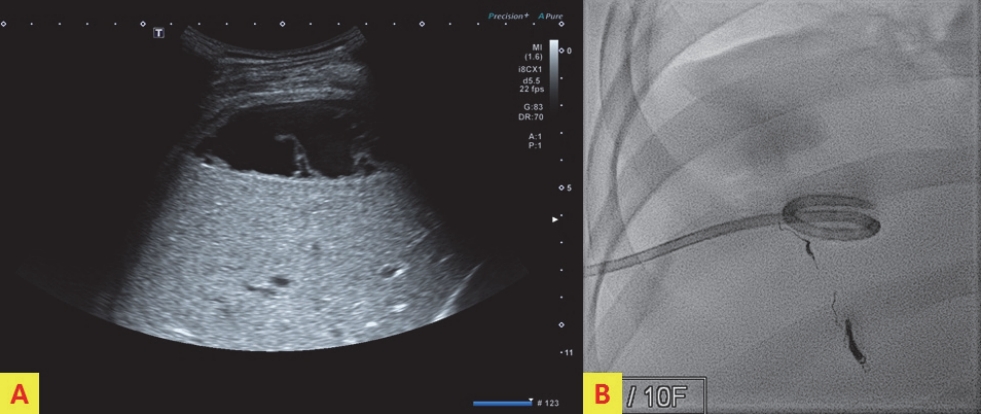
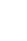
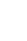
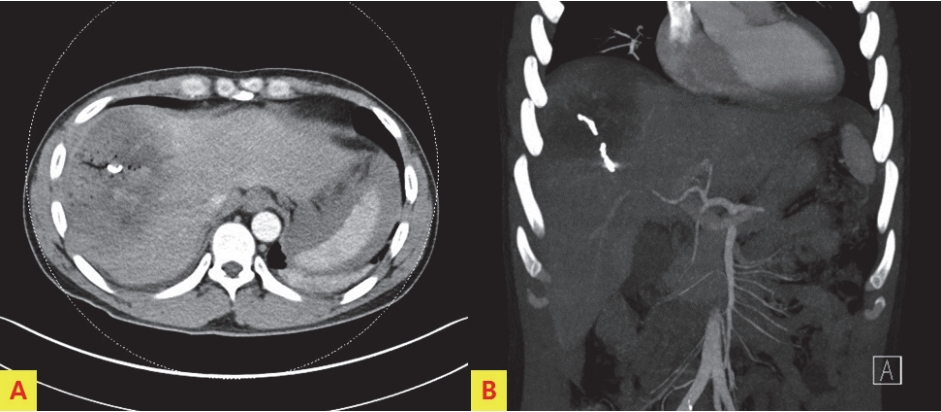
A 41-year-old man presented to the emergency department after a pedestrian traffic accident. The initial vital signs were unstable: systolic blood pressure, 80 mm Hg; pulse rate, 56 beats/min; respiration rate, 16 breaths/min; body temperature, 36.0Ōäā; and oxygen saturation, 95%. Early abdominal computed tomography (CT) of the right side of the liver showed American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) grade IV injury, according to the Organ Injury Scale (OIS) score, with extravasation of contrast material (Fig. 1.). On the same day, hepatic artery angiography showed active bleeding in segments 5, 7, and 8, and embolization was performed (Fig. 2.). Liver enzyme levels (aspartate aminotransferase, 1036 IU/L; alanine transferase, 1192 IU/L) were highest on day 3 after admission. No extravasation of contrast material was observed on abdominal CT performed on day 3 (Fig. 3.). On day 5, the patient developed abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant. The focus of pain was more lateral than the location of the gallbladder on initial abdominal CT, and tenderness was also observed on physical examination. On abdominal ultrasonography, biloma was observed in the hepatic dome. Therefore, percutaneous drainage was performed (Fig. 4.). Biloma was still observed on abdominal CT 2 weeks later (Fig. 5.).
CT and ultrasonography play an important role in the initial treatment of abdominal blunt trauma. CT has high sensitivity for detecting liver parenchymal injuries. However, it is difficult to rule out organ injuries on ultrasonography, even when performed by skilled technicians [1]. Laboratory findings for biloma are nonspecific. If the right upper quadrant abdominal pain, chills, and fever are present in patients with recent abdominal injuries, biloma may be suspected [2]. Biloma appears as a hypodense fluid collection on CT [3]. Ultrasonography reveals a hypoechoic to anechoic fluid collection and well-defined margins findings in the typical location (right upper quadrant abdomen: sub-intrahepatic, below the diaphragm). Color Doppler ultrasonography shows no vascularity [4]. Garcia Urguelles et al. [5] stated that conservative management through percutaneous drainage under ultrasonographic guidance should be the first choice of treatment. In our patient, biloma was first diagnosed on ultrasonography after the patient reported right upper quadrant abdominal pain after blunt liver injury. Conservative management with percutaneous drainage was performed.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Initial abdominal computed tomography, showing American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) grade II liver injury according to the Organ Injury Scale (OIS) score, with extravasation of contrast material in the right side of the liver.

Fig.┬Ā2.
Hepatic artery angiography, showing active bleeding in segments 5, 7, and 8 (A). Embolization was performed at the bleeding focus (B).

Fig.┬Ā3.
No extravasation of contrast material or biloma was observed on abdominal CT performed on day 3 after admission. The coils used for bleeding focus are visible.
REFERENCES
1. Poletti PA, Wintermark M, Schnyder P, Becker CD. Traumatic injuries: role of imaging in the management of the polytrauma victim (conservative expectation). Eur Radiol. 2002;12(5):969-78.


2. Tana C, DŌĆÖAlessandro P, Tartaro A, Tana M, Mezzetti A, Schiavone C. Sonographic assessment of a suspected biloma: A case report and review of the literature. World J Radiol. 2013;5(5):220-5.



3. De Backer A, Fierens H, De Schepper A, Pelckmans P, Jorens PG, Vaneerdeweg W. Diagnosis and nonsurgical management of bile leak complicated by biloma after blunt liver injury: report of two cases. Eur Radiol. 1998;8(9):1619-22.


-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 4,997 View
- 39 Download
-
Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis Following a Traumatic Liver Injury2017 November;2(2)